Embed dependencies in your Assembly
15 Nov 2019Sometimes, when your assembly has many dependencies, you may have the need to simplify deployment. One useful approach is to embed dependent assembly into the main one. To proceed, you need to add the assembly as embedded resource into your project:
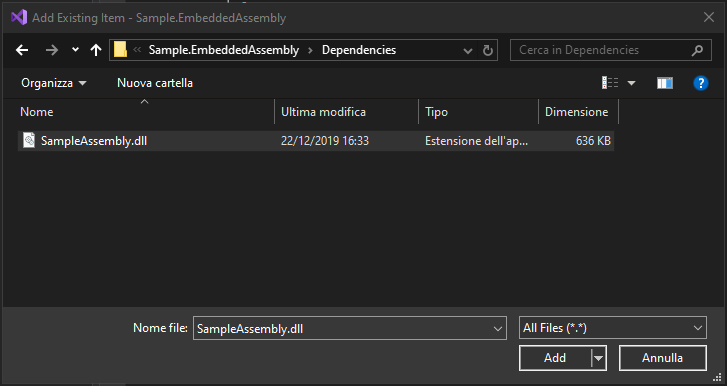
Then set the assembly as Embedded Resource:
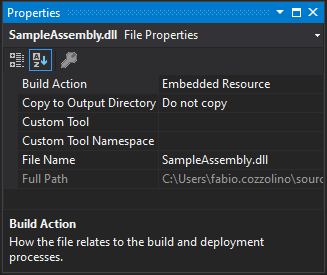
Finally, the code is very simple. Subscribe to the AssemblyResolve event. That event is fired when the common language runtime is unable to locate and bind the requested assembly:
AppDomain.CurrentDomain.AssemblyResolve += new ResolveEventHandler(CurrentDomain_AssemblyResolve);
Then, you must implement the event handler, read the assembly from resources and call the Assembly.Load method to load it:
private Assembly CurrentDomain_AssemblyResolve(object sender, ResolveEventArgs args)
{
string assemblyName = args.Name.Split(',').First();
string assemblyFolder = "Resources";
string assemblyEmbeddedName = string.Format("{0}.{1}.{2}.dll",
this.GetType().Namespace, assemblyFolder, assemblyName);
Assembly currentAssembly = Assembly.GetExecutingAssembly();
using (var stream = currentAssembly.GetManifestResourceStream(assemblyEmbeddedName))
{
if (stream == null)
{
return null;
}
var buffer = new byte[(int)stream.Length];
stream.Read(buffer, 0, (int)stream.Length);
return Assembly.Load(buffer);
}
}
The above code assumes that the assembly are stored in a folder named Resources and the base namespace is the same of the current type.
Conclusion
At the end, we can analyze the pros and cons of this approach:
- Pros
- Reduced set of assemblies to deploy is the main reason that could suggest you to embed it in your assembly
- Cons
- Dependent assemblies needs to be manually updated when new release are available
This is a very simple way to read embedded assemblies. Be careful, use this approach only if it is really necessary.
Enjoy!




