Using DynamoDB local with .NET Aspire and AWS
08 Feb 2025Introduction
Following the first post about .NET Aspire and AWS, I want to explore now the possibility of using AWS resources with .NET Aspire to enable a local development environment that is quite similar to the one available in the cloud. Locally replicating a cloud environment is currently a big challenge for developers. The issue becomes very high if you want to use serverless solutions, like Lambda or DynamoDB. We will see what the current possibilities are with .NET Aspire.
Using DynamoDB Local
With AWS you already have the possibility to use a local version of DynamoDB. It is simple a downloadable version that you can run locally for development and testing purpose. Starting from the 9.1.0 version of the (Aspire.Hosting.AWS NuGet Package)[https://www.nuget.org/packages/Aspire.Hosting.AWS], you also have the option to integrate DynamoDB in your infrastructure.
Following the code that we have seen in the previous post, we can open our AppHost project and write the following C# code in Program.cs:
using Aspire.Hosting.AWS.DynamoDB;
...
var builder = DistributedApplication.CreateBuilder(args);
var localDynamoDB = builder.AddAWSDynamoDBLocal("MyLocalDB");
builder.Build().Run();
Obviously, we can create a dependency by using the WithReference and WaitFor methods, to instruct Aspire that a project, for example ApiService, must wait for the DynamoDB service to be in state READY before starting:
var builder = DistributedApplication.CreateBuilder(args);
var localDynamoDB = builder.AddAWSDynamoDBLocal("MyLocalDB");
builder.AddProject<Projects.AspireOnAWS_ApiService>("api")
.WithExternalHttpEndpoints()
.WithReference(localDynamoDB)
.WaitFor(localDynamoDB);
builder.Build().Run();
Now you can run your project again and look, there is a new kid in town:
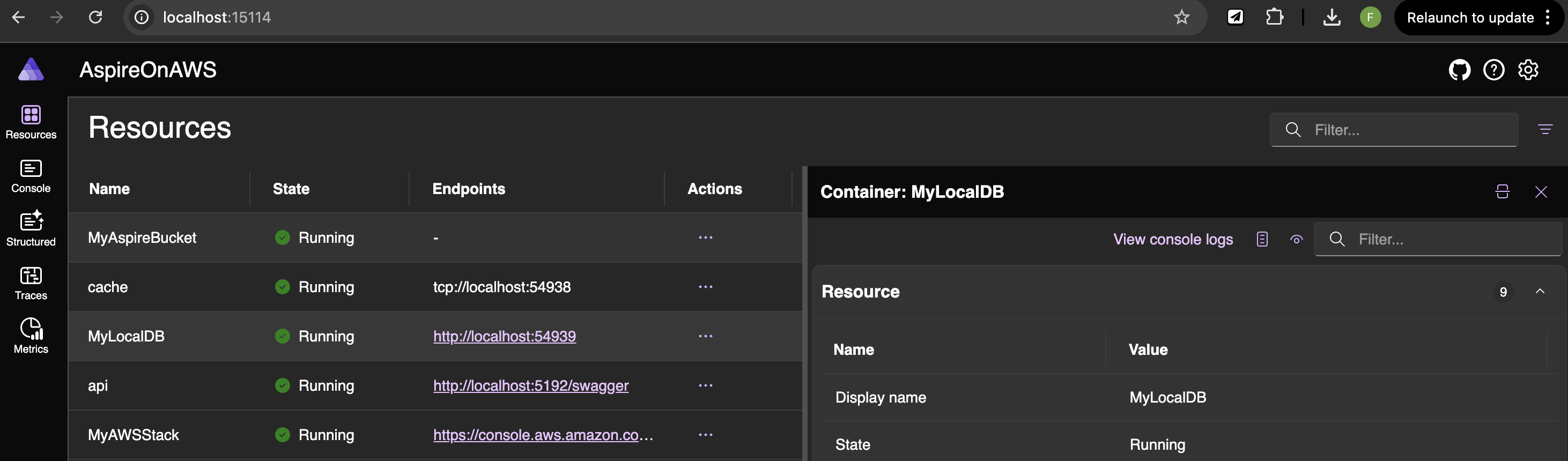
Use DynamoDB Local
To use DynamoDB in ApiService project, you can simply reference the AWSSDK.DynamoDBv2 from the AWS SDK and use the following code:
AmazonDynamoDBClient client = new AmazonDynamoDBClient();
Keep in mind that is very important to not set RegionEndpoint. If no Region is provided, the SDK will search the environment for configuration details that define the location of the DynamoDB service. Furthermore, the Service-specific endpoints feature provided by AWS SDKs allows setting an endpoint by using an environment variable.
The AWS_ENDPOINT_URL_DYNAMODB environment variable will be set in the local container and it is injected to the .NET project by using the WithReference method call. That’s magic!
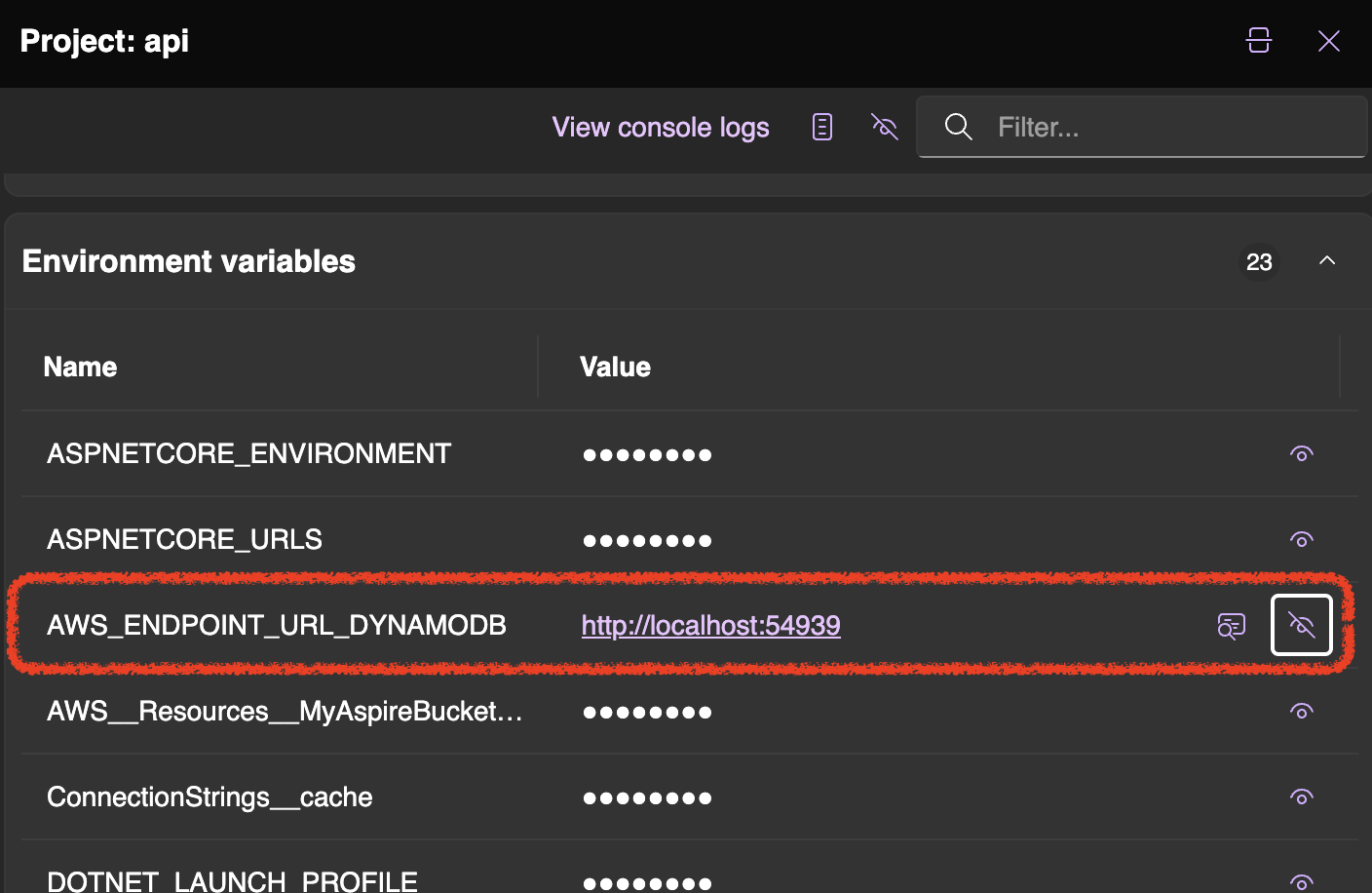
Now you can use DynamoDB also with local environment with very minimal impact on code.
Conclusion
.NET Aspire is becoming a very big asset in our developer portfolio. We are looking forward to the new feature that will be developed and integrated also in the AWS package. I’ll write again about that. In the meantime, let me know your experience and what you would like to have in the package.
Enjoy!




